BLOG
Communication frameworks in Smart lighting systems

Shreya Dr
Sept 25, 2021 4 min read
A smart street lighting system comprises a network of street lights that are virtually connected to a lighting management system. Such a system consists of hardware and software, working in tandem to provide energy savings and operational efficiencies. The competitive advantage of an IoT-enabled lighting system over a conventional lighting system comes with its ability to offer remote control and real-time status of the lighting network. The basic components of such a system include high-efficiency LED lamps, an IoT-based communication network, and smart sensors for additional features. The lighting controller is the key component of every smart lighting installation, they are devices that allow users to control street lights and at the same time receive valuable feedback.
Several communication technologies such as RF Zigbee, PLCC, GSM, LoraWan, and NBIoT are incorporated to facilitate communication between the street light controller and the lighting management system. Hynetic Electronics provides an end-to-end solution for smart street lighting that is tailored to meet customer requirements. A suitable communication framework can be deployed by taking into consideration certain factors like site conditions, the number of lights, operational and capital expenses, etc.
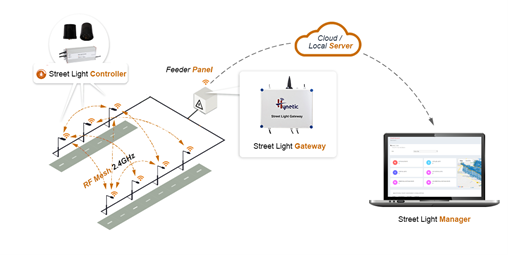
The choice of the communication technology depends on the aforementioned factors and the specific situation under consideration. For instance, RF-Zigbee technology is suitable only when all consecutive lights are Smart RF Enabled. Such a communication protocol will not be suitable for randomly distributed Smart lighting implementation. In addition, RF-ZigBee technology is developed to cater to the needs of low-cost and low-power IoT applications. Zigbee is used in devices where a low data rate and secure networking are needed. This network uses “multi-hop” routing to reach far distances and this Mesh topology ensures that it is perfectly suited for Smart Street Lighting applications. Another added advantage of this communication technology is the ease of deployment and low operational costs (OPEX). Fig 1 gives an illustration of an RF-Zigbee-based smart lighting system.
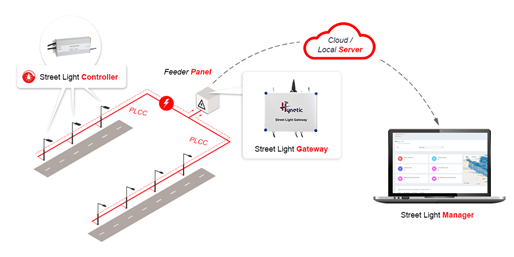
PLCC( Power line carrier communication) is a communication framework with a simple infrastructure, it’s a wired communication technique that can facilitate communication through existing power lines. Advantages of such a system include elimination of shared bandwidth, ease of deployment, no line-of-sight limitation, and easy fault detection. Hynetic Electronics incorporates PLCC to deploy smart lighting systems with an aim to conserve power, reduce maintenance costs and provide rapid payback to operators and the environment. Fig 2 gives an illustration of this communication framework.
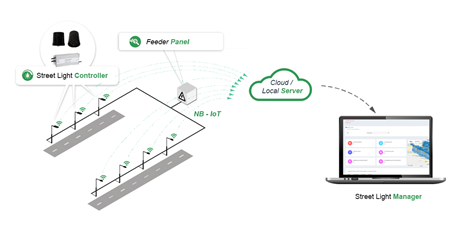
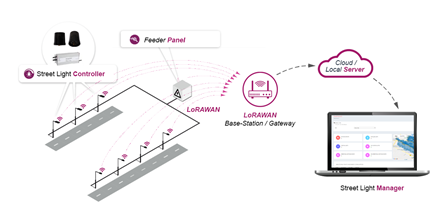
LoraWAN is a network (protocol) based on the LoRa technology, LoRa is a proprietary low power wide area modulation technique based on CSS( chirp spread spectrum technology). The LoRaWAN framework targets key requirements of IoT such as secure bi-directional communication, mobility, and localization services. Some of the key benefits include low power consumption that leads to better battery life, ease of deployment, a wide coverage range that enables smart city applications, greater security, and low bandwidth that makes it ideal for IoT frameworks with low data rates. LoRaWAN technology would therefore be ideal for applications that are noncritical and delay-tolerant, uplink oriented, and battery-powered. Hynetics’ LoRaWAN solution can be connected with leading network providers like Tata Communications Ltd and Senra for PAN-India deployments.
It’s impossible to claim that one technology is superior to another. Every technology has its pros and cons. A brief comparison of all the technologies will give an overview of their features.
A selection of a particular communication framework can be made based on factors such as:
- Network Topology
- Street Light Gateway Requirement
- Control Latency
- Operational
- Capital expenses etc.
Table 1 gives a tabulated summary of the main features that need to be considered before selection. A pro-con analysis for each communication framework has also been summarised.
Table 1. Comparison of communication technologies
| FEATURES | COMMUNICATION FRAMEWORK | |||
| RF | GSM – GRPS [2G & 4G] | PLCC | LoRaWAN | |
| Network Topology | – Wireless – 2.4GHz / 865MHz – RF Mesh | – Wireless – Quad-band GSM / 4G band | – Wired – 2MHz – 30MHz band | – Wireless – 865MHz – 867MHz |
| Street Light Gateway Requirement | Required | Not Required | Required | Not Required |
| Communication between SLC & SLG | RF Mesh | Not Applicable Communicates through 2G/4G mobile base-stations | Through existing power line No additional wires required | Not Applicable Communicates through LoRaWAN base-stations |
| Communication between Server & SLC | Through SLG | Communicates through 2G/4G mobile base-stations | Through SLG | Communicates through LoRaWAN base-stations |
| Control Latency | – Medium – 30 secs to 3 minutes* *Depending on network bandwidth between SLG & Server | – Low – 15 secs to 3 minutes* *Depending on the 2G & 4G connectivity at that point of time | – Medium – 30 secs to 3 minutes* *Depending on network bandwidth between SLG and Server | – High – 1 minute – 10 minutes* *Depending on LoRaWAN base-station & network |
| Periodic Data Collection Latency | 8 minutes to 15 minutes per light node *Assuming 50 lights per gateway | As low as 1 minute depending on the configuration | 8 minutes to 15 minutes per light point *Assuming 50 lights per gateway | Theoretically, it is possible to push the data every 1 minute from each light node. Practically, it depends on the limitations of the number of uploads per day defined by the network provider Communication latency to the Server depends on the LoRaWAN base-station |
| Ease of Deployment | Easy / Medium Network formation and assignment of SLCs to SLG is required during commissioning | Very Easy | Easy / Medium Assignment of SLCs to SLG is required during commissioning | Easy |
| Capital Expenses (Unit Cost) | X | X – 10% (for 2G) 4X (for 4G) | X + 10% | X – 5% |
| Operating Expenses | – Less – Operating cost associated with SIM cards is only for SLG | – Medium / High – Operating cost associated with SIM cards for all SLCs | – Less -Operating cost associated with SIM cards is only for SLG | – Medium / High – Operating cost of LoRaWAN network |
| Pros | – Strong mesh network topology – Less operating costs | – Easy to deploy & hassle-free commissioning – Faster communication to the Server – GPS add-on available for accurate location positioning | – Strong network between SLC & SLG – No external antennas required – Less operating costs | – Easy to deploy & hassle-free commissioning |
| Cons | – Commissioning support required – Periodic data collection is slightly higher than the GSM-GPRS variant | – Higher operating expenses – 4G variant is extremely expensive | – Commissioning support required – Periodic data collection is slightly higher than the GSM-GPRS variant | – Higher operating expenses due to LoRaWAN network |
Please enter your details below to access these blog resources.
Any questions please contact info@hynetic.com.
Thank You!
Do you need a smart street lighting solution?
Let us help you identify and evaluate the technical solutions that will help you reach your smart lighting and smart city goals.